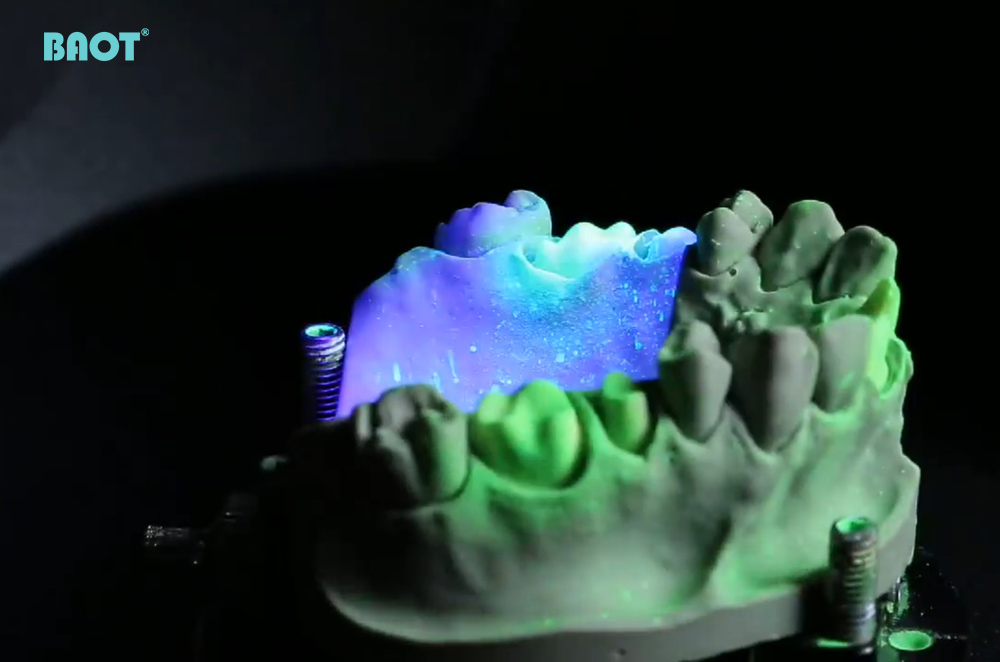
In modern dental laboratories, dental desktop scanners have become indispensable tools. These devices use high-precision scanning technology to convert physical tooth models, impressions, and restorations into three-dimensional digital models, greatly enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of dental restorations and designs. Today, we will delve into dental desktop scanners' basic principles and working mechanisms.
Working Principles
Dental desktop scanners primarily use optical or laser scanning technology to capture the three-dimensional data of physical models. Here are the basic steps involved:
1. Scanning Preparation:
- First, the tooth model or impression to be scanned is placed on the scanner's platform. Ensuring the model is securely fixed is crucial to avoid movement during the scanning process.
2. Data Capture:
- Once the scanner is activated, it emits light (such as white light, blue light, or laser) onto the surface of the model. The reflected light from the model's surface is received by the scanner's camera or sensor.
- The scanner captures the three-dimensional shape of the model by measuring the changes in the reflected light. Most modern scanners use multi-angle scanning to ensure all details of the model are captured.
3. Data Processing:
- The scanner transmits the captured point cloud data to a computer, where specialized software processes and integrates the data.
- The software converts the point cloud data into a three-dimensional mesh model, forming a detailed digital tooth model.
4. Digital Model Generation:
- After data processing and optimization, the generated three-dimensional digital model can be used for designing and manufacturing dental restorations.
- This digital model can also be integrated with CAD/CAM systems for further design and manufacturing processes.
Types of Scanning Technology
1. Optical Scanning:
- Uses white light or blue light for scanning, suitable for capturing high-precision details. Optical scanners typically offer fast scanning speeds and high resolution.
- Commonly used in the design of restorations and the scanning of complex-shaped models.
2. Laser Scanning:
- Uses a laser beam to scan the object's surface and obtain three-dimensional data through laser reflection. Laser scanners excel in scanning precision and depth perception.
- Particularly suitable for designing implants and guides that require extremely high precision.
Advantages of Dental Desktop Scanners
- High Precision: Capable of capturing extremely fine details, ensuring a perfect fit for restorations.
- High Efficiency: Fast scanning and data processing significantly shorten the design and manufacturing cycle.
- Error Reduction: Digital workflows reduce errors inherent in traditional manual processes, improving the quality and stability of restorations.
In summary, dental desktop scanners use high-precision optical and laser scanning technologies to digitize physical models, providing powerful tools for dental restoration and design. They not only improve work efficiency but also enhance the precision of treatments, offering better outcomes for patients. With continuous technological advancements, dental desktop scanners will play an increasingly important role in the dental field.
